Earnings Per Share (EPS) and its role in Dividend Growth Investing (DGI)

Earnings Per Share (EPS) and its role in Dividend Growth Investing (DGI)
When analyzing dividend growth stocks, one of the most important financial metrics to consider is Earnings Per Share (EPS). EPS is a key indicator of a company’s profitability and plays a crucial role in determining whether a company can sustain and grow its dividends over time. That is why EPS falls in the Pillar of Risk in the Blueprint. (Sign up , free, and download this easy to follow blueprint for navigating the complexity of picking stocks like a pro)
In this article, we’ll explore what EPS is, why it matters for dividend investors, and how you can use it to make smarter investment decisions.
What is Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
EPS measures how much profit a company generates for each outstanding share of its stock. It’s calculated using the following formula:
EPS = (Net Income - Preferred Dividends) / Total Outstanding Shares
Types of EPS:
- Basic EPS: Uses the total number of outstanding shares.
- Diluted EPS: Adjusts for potential shares from convertible securities (e.g., stock options, convertible bonds).
- Trailing EPS: Based on the last 12 months of earnings.
- Forward EPS: Estimates future earnings based on projections.
Why Does EPS Matter for dividend investors?
EPS is a key metric for assessing a company’s profitability, which directly influences its ability to pay and grow dividends. Here’s why it matters:
1. Indicator of profitability
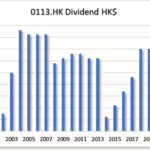
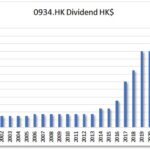
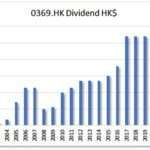
A consistently growing EPS suggests that a company is making more money, which increases the likelihood that it can sustain and raise dividends.
2. Dividend sustainability
A company cannot pay dividends indefinitely if its earnings are shrinking. By monitoring EPS trends, investors can assess whether a company has the financial strength to maintain or increase its dividend payouts.
3. EPS and the payout ratio
EPS is closely tied to the dividend payout ratio, which is calculated as:
Payout Ratio = (Dividends Per Share / Earnings Per Share) × 100%
A payout ratio below 50% is generally considered sustainable, leaving room for future dividend growth. A payout ratio above 80% could signal potential risk if earnings decline.
4. EPS Growth and dividend growth
Companies with stable or growing EPS are more likely to increase their dividends over time. To assess long-term sustainability, we look at 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year EPS growth trends.
EPS Benchmarks for Dividend Growth Investing
When evaluating stocks for dividend growth potential, we use the following EPS-related benchmarks:
- EPS > 0.001 → Indicates the company is profitable.
- EPS Growth > 1% (1-year, 3-year, and 5-year) → Suggests sustainable earnings expansion.
- Dividend Payout Ratio < 50% → Ensures earnings can support dividends without excessive strain.
- Return on Equity (ROE) > 10% → Measures profitability relative to shareholder equity.
- Dividend Coverage Ratio > 2 → Confirms earnings can comfortably cover dividend payments.
How to Use EPS in stock analysis
Step 1: Check EPS trends
Look at the company’s EPS over multiple years. A steady increase indicates strong financial health, while erratic or declining EPS could be a warning sign.
Step 2: Compare EPS to Dividend Growth
If dividends are growing but EPS is not, it could indicate an unsustainable payout policy.
Step 3: Analyze EPS Relative to industry peers
Compare a company’s EPS growth to competitors in the same industry. A company with stronger earnings growth than peers is likely in a better financial position.
Step 4: Combine EPS with other key metrics
EPS should be analyzed alongside Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio, Dividend Payout Ratio, and Debt-to-Equity Ratio to get a complete picture of a stock’s financial health.
Common pitfalls when evaluating EPS
- EPS can be manipulated – Companies can use accounting tactics to artificially inflate EPS. Look at Free Cash Flow (FCF) for a more accurate picture.
- One-Time gains or losses – Avoid making decisions based on temporary EPS spikes or declines caused by asset sales, write-offs, or restructuring costs.
- Diluted EPS vs. Basic EPS – Always check diluted EPS, which accounts for potential stock dilution.
Conclusion
Earnings Per Share (EPS) is a fundamental metric in dividend growth investing. A strong, growing EPS supports a company’s ability to maintain and increase its dividend payments. By incorporating EPS analysis into your investment strategy, you can identify financially stable companies that offer sustainable, long-term dividend growth.
If you’re serious about building a dividend growth portfolio, our stock screener simplifies this process. Become a Champion member today to access our curated list of Hong Kong dividend growth stocks analyzed through the three-pillar framework: Growth, Risk, and Value.
Join Now to start making smarter dividend investment decisions!

Sign up now and get immediate access to
25 highest yield dividend growth stocks.xls
The Best Part?
It’s completely free. No catch—just honest, data-driven insights that arm you with a consistent approach to dividend growth investing.